GenQ
在我们的论文 BEIR:一个用于信息检索模型零样本评估的异构基准中,我们提出了一种方法,用于为一个没有标记训练数据的语料库调整模型,以进行非对称语义搜索。
背景
在非对称语义搜索中,用户提供一个(简短的)查询,如一些关键词或一个问题。然后我们希望检索到提供答案的较长文本段落。
例如
query: What is Python?
passage to retrieve: Python is an interpreted, high-level and general-purpose programming language. Python's design philosophy emphasizes code readability with its notable use of significant whitespace. Its language constructs and object-oriented approach aim to help programmers write clear, logical code for small and large-scale projects.
我们已经在这里展示了当有足够的训练数据(查询 & 相关段落)时如何训练这类模型:训练 MS MARCO 数据集
在本教程中,我们将展示在没有可用训练数据的情况下如何训练这类模型,也就是说,如果您没有成千上万个带标签的查询 & 相关段落对。
概述
我们使用合成查询生成来达到我们的目标。我们从文档集合中的段落开始,创建用户可能询问或搜索的可能查询。
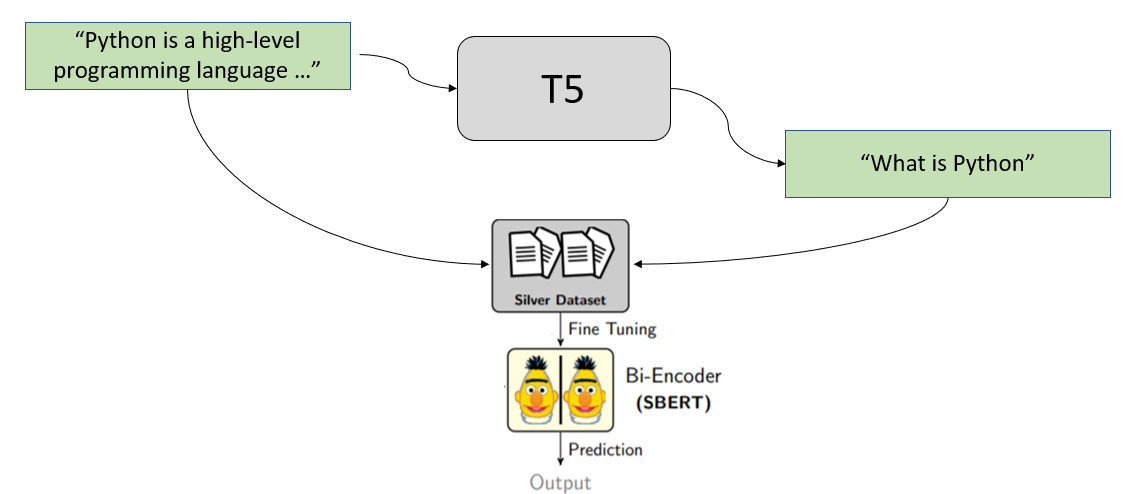
例如,我们有以下文本段落
Python is an interpreted, high-level and general-purpose programming language. Python's design philosophy emphasizes code readability with its notable use of significant whitespace. Its language constructs and object-oriented approach aim to help programmers write clear, logical code for small and large-scale projects.
我们将这个段落传递给一个经过专门训练的 T5 模型,它会为我们生成可能的查询。对于上面的段落,它可能会生成这些查询
什么是 python
python 的定义
什么语言使用空白
然后我们使用这些生成的查询来创建我们的训练集
(What is python, Python is an interpreted...)
(definition python, Python is an interpreted...)
(what language uses whitespaces, Python is an interpreted...)
并用它来训练我们的 SentenceTransformer 双编码器。
查询生成
在 BeIR 中,我们提供了可用于查询生成的不同模型。在这个例子中,我们使用由 docTTTTTquery 训练的 T5 模型。
from transformers import T5Tokenizer, T5ForConditionalGeneration
import torch
tokenizer = T5Tokenizer.from_pretrained("BeIR/query-gen-msmarco-t5-large-v1")
model = T5ForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained("BeIR/query-gen-msmarco-t5-large-v1")
model.eval()
para = "Python is an interpreted, high-level and general-purpose programming language. Python's design philosophy emphasizes code readability with its notable use of significant whitespace. Its language constructs and object-oriented approach aim to help programmers write clear, logical code for small and large-scale projects."
input_ids = tokenizer.encode(para, return_tensors="pt")
with torch.no_grad():
outputs = model.generate(
input_ids=input_ids,
max_length=64,
do_sample=True,
top_p=0.95,
num_return_sequences=3,
)
print("Paragraph:")
print(para)
print("\nGenerated Queries:")
for i in range(len(outputs)):
query = tokenizer.decode(outputs[i], skip_special_tokens=True)
print(f"{i + 1}: {query}")
在上面的代码中,我们使用了 Top-p (nucleus) 采样,它会从一组可能的词中随机选择一个词。因此,该模型每次都会生成不同的查询。
双编码器训练
利用生成的查询,我们可以使用 MultipleNegativesRankingLoss 来训练一个双编码器。
完整示例
我们训练一个语义搜索模型来搜索关于编程文章和技术的维基百科文章。
我们使用以下维基百科文章的文本段落:Assembly language, C , C# , C++, Go , Java , JavaScript, Keras, Laravel, MATLAB, Matplotlib, MongoDB, MySQL, Natural Language Toolkit, NumPy, pandas (software), Perl, PHP, PostgreSQL, Python , PyTorch, R , React, Rust , Scala , scikit-learn, SciPy, Swift , TensorFlow, Vue.js
在
1_programming_query_generation.py - 我们为这些文章的所有段落生成查询
2_programming_train_bi-encoder.py - 我们用这些生成的查询训练一个 SentenceTransformer 双编码器。这将产生一个我们可以用于语义搜索(针对给定的维基百科文章)的模型。
3_programming_semantic_search.py - 展示了如何使用训练好的模型进行语义搜索。